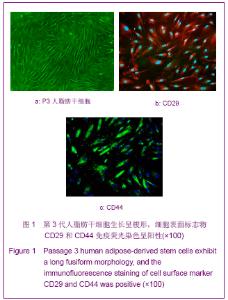
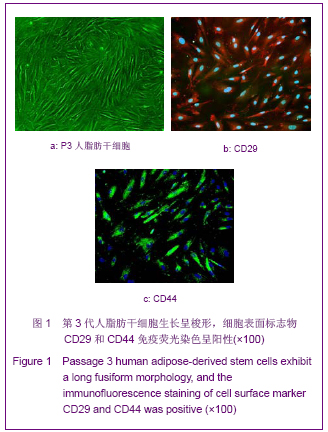
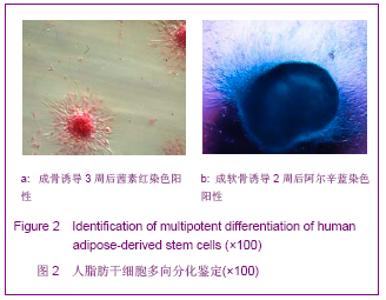
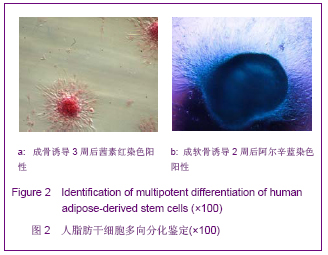
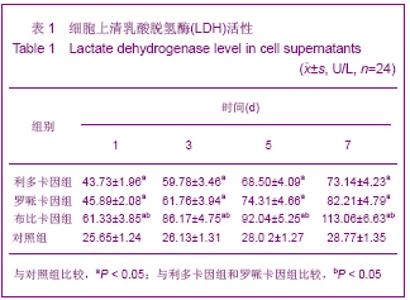
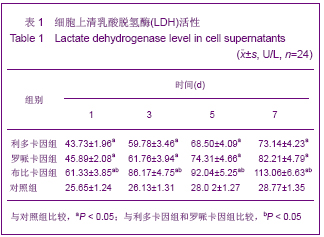
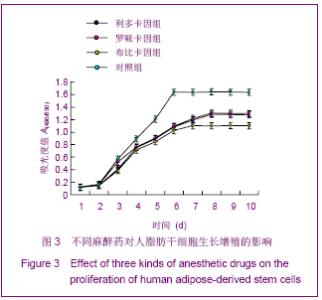
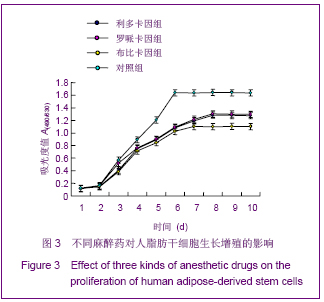
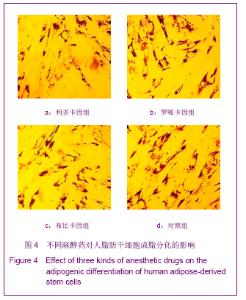
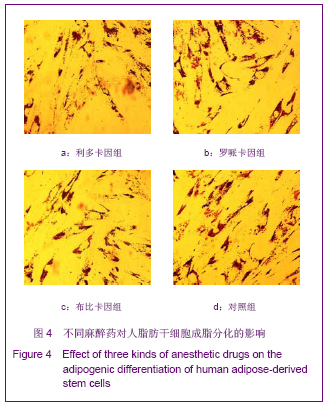
| [1] Korn BS, Kikkawa DO, Hicok KC. Identification and characterization of adult stem cells from human orbital adipose tissue. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg. 2009;25(1):27-32.[2] Mizuno H. Adipose-derived stem cells for tissue repair and regeneration: ten years of research and a literature review. J Nippon Med Sch. 2009;76(2):56-66.[3] Lu F, Mizuno H, Uysal CA, et al. Improved viability of random pattern skin flaps through the use of adipose-derived stem cells. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2008;121(1):50-58.[4] Francis MP, Sachs PC, Elmore LW, et al.Isolating adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells from lipoaspirate blood and saline fraction. Organogenesis. 2010;6(1):11-14.[5] Li HM, Gao JH, Lu F, et al. Zhongguo Xiufu Chongjian Waike Zazhi. 2009;23(2):161-165.黎洪棉,高建华,鲁峰,等.两种不同肌筋膜瓣包裹脂肪来源干细胞载体复合物体内成脂效率的比较研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志, 2009,23(2):161-165.[6] Li HM, Liu DL, Yu YL, et al. Zhongguo Xiufu Chongjian Waike Zazhi. 2009;23(6):732-736.黎洪棉,柳大烈,余元龙,等.自体PRP 促进人脂肪来源干细胞成骨分化的体外实验研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2009,23(6): 732-736.[7] Li HM, Gao JH, Lu F, et al. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2009;13(25):4829-4833.黎洪棉,高建华,鲁峰,等.海绵状Ⅰ型胶原蛋白与兔脂肪干细胞的生物相容性[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009,13(25): 4829-4833.[8] Li HM, Gao JH, Yu YL, et al. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2009;13(36):7025-7028.黎洪棉,高建华,余元龙,等.大鼠脂肪干细胞定向分化为成骨细胞及体外增殖过程中地塞米松的抑制性干预[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009,13(36):7025-7028.[9] Zuk PA, Zhu M, Mizuno H et al, Multilineage cells from human adipose tissue: implications for cell-based therapies. Tissue Eng. 2001;7:221-228. [10] Caviggioli F, Vinci V, Salval A, et al. Human adipose-derived stem cells: isolation, characterization and applications in surgery. ANZ J Surg. 2009;79(11):856.[11] Pountos I, Georgouli T, Giannoudis PV. The effect of autologous serum obtained after fracture on the proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 2008;26,54(1):33-39.[12] Arrigoni E, Lopa S, de Girolamo L,et al. Isolation, characterization and osteogenic differentiation of adipose-derived stem cells: from small to large animal models. Cell Tissue Res. 2009;338(3):401-411.[13] Kuhbier JW, Weyand B, Radtke C, et al.Isolation, characterization, differentiation, and application of adipose-derived stem cells. Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol. 2010; 123:55-105.[14] Vieira NM, Brandalise V, Zucconi E,et al. Isolation, characterization, and differentiation potential of canine adipose-derived stem cells. Cell Transplant. 2010;19(3): 279-289.[15] Moseley TA, Zhu M, Hedrick MH. Adipose-derived stem and progenitor cells as fillers in plastic and reconstructive surgery. Plast Reconstr Surg.2006;118(3 Suppl):121S-128S.[16] Vallée M, Côté JF, Fradette J. Adipose-tissue engineering: taking advantage of the properties of human adipose-derived stem/stromal cells. Pathol Biol (Paris). 2009;57(4):309-317.[17] Vermette M,Trottier V,Menard V,et al.Production of a new tissue-engineered adipose substitute from human adipose-derived stromal cells.Biomaterials.2007; 28(18): 2850-2860. [18] De Ugarte DA, Morizono K, Elbarbary A, et al.Comparison of multi-lineage cells from human adipose tissue and bone marrow.Cells Tissues Organs. 2003;174(3):101-109. [19] Lin SD, Wang KH, Kao AP. Engineered adipose tissue of predefined shape and dimensions from human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells.Tissue Eng Part A. 2008;14(5):571-581.[20] Tobita M, Uysal AC, Ogawa R, et al.Periodontal tissue regeneration with adipose-derived stem cells.Tissue Eng Part A.2008;14(6):945-953.[21] Francis MP, Sachs PC, Elmore LW, et al.Isolating adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells from lipoaspirate blood and saline fraction. Organogenesis. 2010;6(1):11-14.[22] Mizuno H. Adipose-derived stem and stromal cells for cell-based therapy: current status of preclinical studies and clinical trials. Curr Opin Mol Ther. 2010;12(4):442-449.[23] Zuk PA. The adipose-derived stem cell: looking back and looking ahead. Mol Biol Cell. 2010;21(11):1783-1787.[24] Cousin B, André M, Arnaud E,et al.Reconstitution of lethally irradiated mice by cells isolated from adipose tissue. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.2003;301(4):1016-1022. [25] Ogawa R,Mizuno H,Watanabe A,et al.Osteogenic and chondrogenic differentiation by adipose-derived stem cells harvested from GFP transgenic mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.2004;313(4):871-877.[26] McIntosh K,Zvonic S,Garrett S,et al.The immunogenicity of human adipose-derived cells:temporal changes in vitro.Stem Cells. 2006;24(5):1246-1253. [27] Kim JM,Lee ST,Chu K,et al.Systemic transplantation of human adipose stem cells attenuated cerebral inflammation and degeneration in a hemorrhagic stroke model.Brain Res. 2007;1183C:43-50.[28] Cao Y, Sun Z, Liao L,et al. Human adipose tissue-derived stem cells differentiate into endothelial cells in vitro and improve postnatal neovascularization in vivo.Biochem Biophys Res Commun.2005;332(2):370-379. [29] Suga H,Shigeura T,Matsumoto D,et al. Rapid expansion of human adipose-derived stromal cells preserving multipotency.Cytotherapy.2007;9(8):738-745. [30] de Girolamo L,Sartori MF,Albisetti W,et al. Osteogenic differentiation of human adipose-derived stem cells: comparison of two different inductive media. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2007;1(2):154-157. |